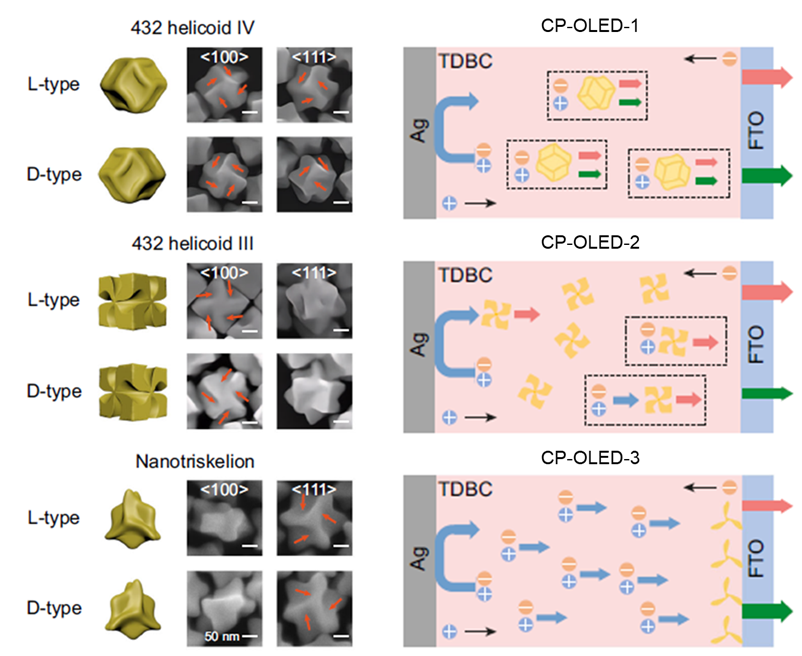
Recently, Zheng Jiapeng, associate professor from the School of Artificial Intelligence Science and Technology, USST, together with Professor Wang Jianfang from the Chinese University of Hong Kong and Professor Shao Lei from Sun Yat-sen University, published an important research result titled "Circularly polarized OLEDs from chiral plasmonic nanoparticle molecule hybrids prepared by chiral plasmonic nanoparticle molecule hybrid system" in the journal Nature Communications. Researchers ingeniously integrated specially-designed spiral-shaped metal nanoparticles into ordinary OLED devices, successfully making the devices directly emit circularly polarized light with rotational characteristics. Zheng is the first author, Professors Wang Jianfang and Professor Shao Lei are the corresponding authors, and USST is the first institution.
Circularly polarized light has broad application prospects in fields such as optical information processing, display imaging, chiral drug synthesis and detection. Traditional circularly polarized OLEDs always struggle to balance brightness and circularly polarized characteristics, just as traditional gasoline-powered cars struggle to achieve both low-fuel consumption and strong power. The innovative technology of the joint research team, known as "adding spiral seasoning to OLED", has got away from industrial dilemma. By designing three different kinds of spiral-shaped metal nanoparticles, a luminescence efficiency of 2.5% and an asymmetry factor of 0.3 were ultimately achieved, solving the technical problem of both brightness and maintaining the spiral characteristics of light emission. It is particularly emphasized that the research team has also confirmed for the first time the close relationship between the geometric morphology and optical properties of metal nanoparticles and device performance.
This display technology that can directly emit circularly polarized light has demonstrated potential applications in multiple fields, paving new paths for the miniaturization of future electronic devices. It can not only make the imaging of AR glasses more three-dimensional and realistic, but can also be used to develop portable medical detection devices, which may bring revolutionary changes to display technology in the future.
Related: https://en.usst.edu.cn/info/1061/3070.htm