September 24, 2021
| By School of Materials and Chemistry | Copyedited by William, Zhang Liu
Recently, Dr. Wang Shige from School of Materials Science, USST, worked with Professor Dionisio Zaldivar-Silva, Vice President of Universidad De La Habana, Academician Li Zhaoshen, Navy Medical University, Director Lu Xuhua, Changzheng Hospital, Naval Military Medical University, and published an academic paper entitled “An injectable anti-microbial and adhesive hydrogel for the effective noncompressible visceral hemostasis and wound repair” in SCI journal Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications(IF=7.328).
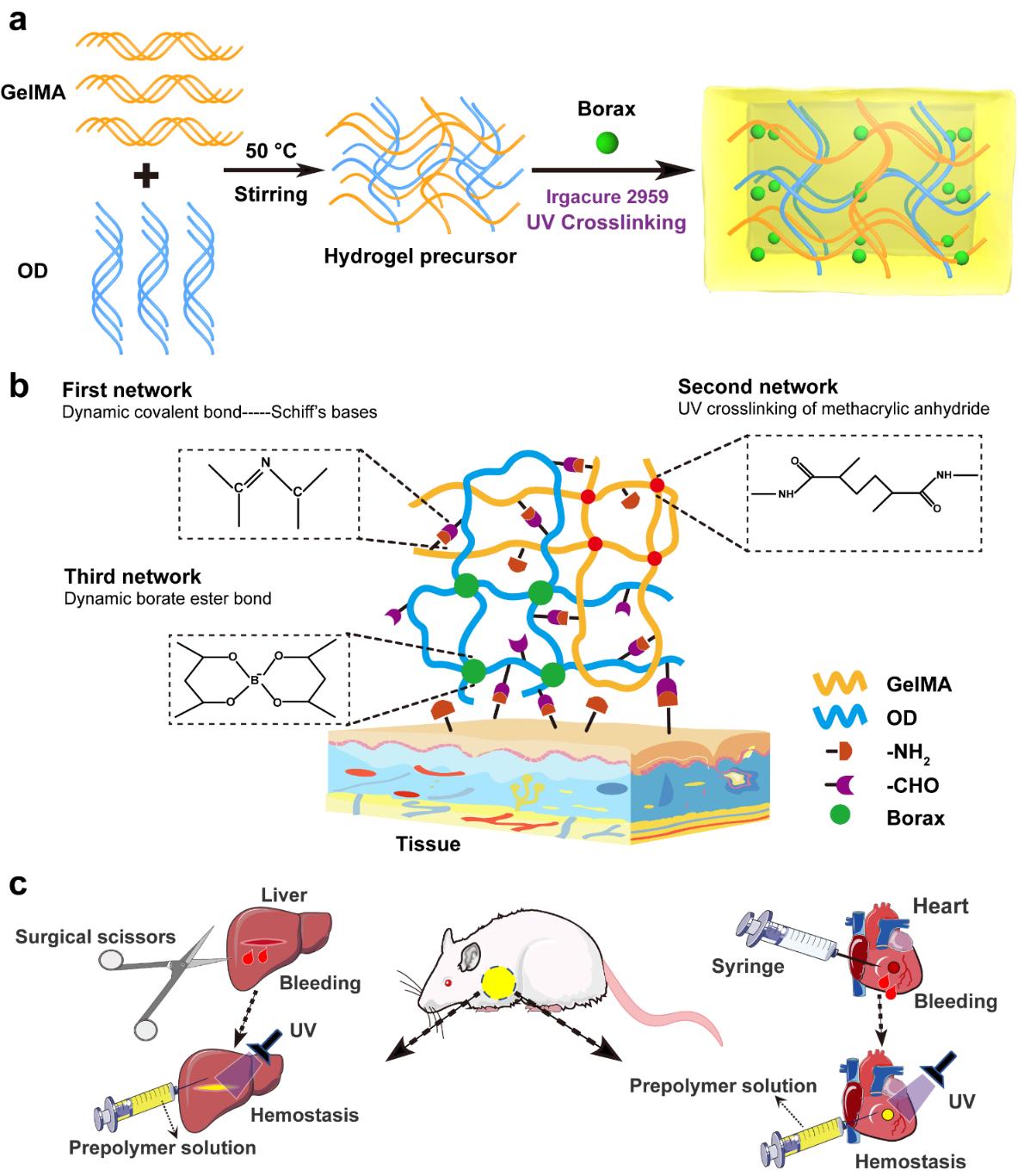
Acute massive bleeding and related wound infection remain one of the main lethal factors worldwide. The rupture of internal arteries of organs is featured with uncontrollable and massive bleeding, high blood and hard self-healing. Hydrogel, which has a three dimensional network, is considered as an ideal platform for wound treatment since it could promote the formation of new blood vessels and tissues and promote the wound healing. In this study, the team designed a GeIMA/oxidized dextran (OD)/sodium tetraborate (Borax) hydrogel as a strong tissue adhesive platform. GeIMA/OD/Borax hydrogel showed an enhanced antibacterial effect through an “adhering and killing” manner, which provides a promising strategy for the design of antimicrobial dressing materials.
Dr. Wang Shige actively carried out work in the basic and applied research of polymer hydrogel materials in wound dressing, drug delivery and tissue engineering together with Professor Dionisio Zaldivar Silva, and senior researcher Lissette Agüero Luztonó from Department of Polymer Materials, Biological Materials Center. The research paper is a phase result. Dr. Wang Shige, Dr. Zhao Jiulong and Director Lu Xuhua were all the corresponding authors. The research work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation, the Shanghai Rising-star Program, sponsored by Shanghai Sailing Program, Naval Medical University Sailing Program and Shanghai Changhai Hospital Youth Fund.
Link to the paper: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493121005622

 Home
·
News & Events
·
Content
Home
·
News & Events
·
Content