Recently, Global Scholars Website announced the rank of global talents, with academic papers and its deep analysis as the core scoring standard. The bibliographical references of all scientists are available to the public, making readers trace and check the data accuracy. Dr.Zhang’s to be chosen achieved a breakthrough in the field of Environment Science and Engineering.
Dr.Zhang Xiaodong, Associate Professor of School of Environment and Architecture, Master’s Supervisor, Winner of Shanghai Youth May Fourth Medal, Shanghai Youth Science and Technology Talent Star Program and Shanghai Yangfan Plan. He is committed to the research of VOCs pollution control and environmentally functional materials synthesis and application. He has published more than 110 SCI papers in journals such as Applied Catalysis B-Environmental and Journal of Catalysis as the first author and corresponding author, of which 35 papers rank among ESI highly cited papers and 21 papers rank among hot papers.
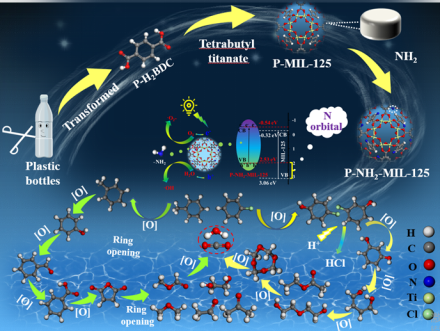
Dr.Zhang Xiaodong worked together with Dr. Liu Ning to publish academic paper in international top journal: Applied Catalysis B-Environmental (IF:19.503). In this study, we used plastic-based terephthalic acid for the synthesis of MIL-125, which further modified by the -NH2 and -NO2 groups. DFT calculations revealed that the N orbitals had an important contribution in reducing the band gap, leading to easier hydrogen absorption and high electron transfer efficiency. Optical studies, XPS, TRES, NH3-TPD and pyridine IR further demonstrated that the amino modification promoted the visible absorption range and acidity of MIL-125 in comparison to the nitro modification, resulting in efficient catalytic degradation of chlorobenzene and toluene, even in the presence of water. This work provides an economically feasible strategy for modifying metal organic frameworks (MOFs) and suggests the possible VOCs degradation pathways with EPR, in situ FTIR, GC-MS and TG-MS analysis.

 Home
·
News & Events
·
Content
Home
·
News & Events
·
Content