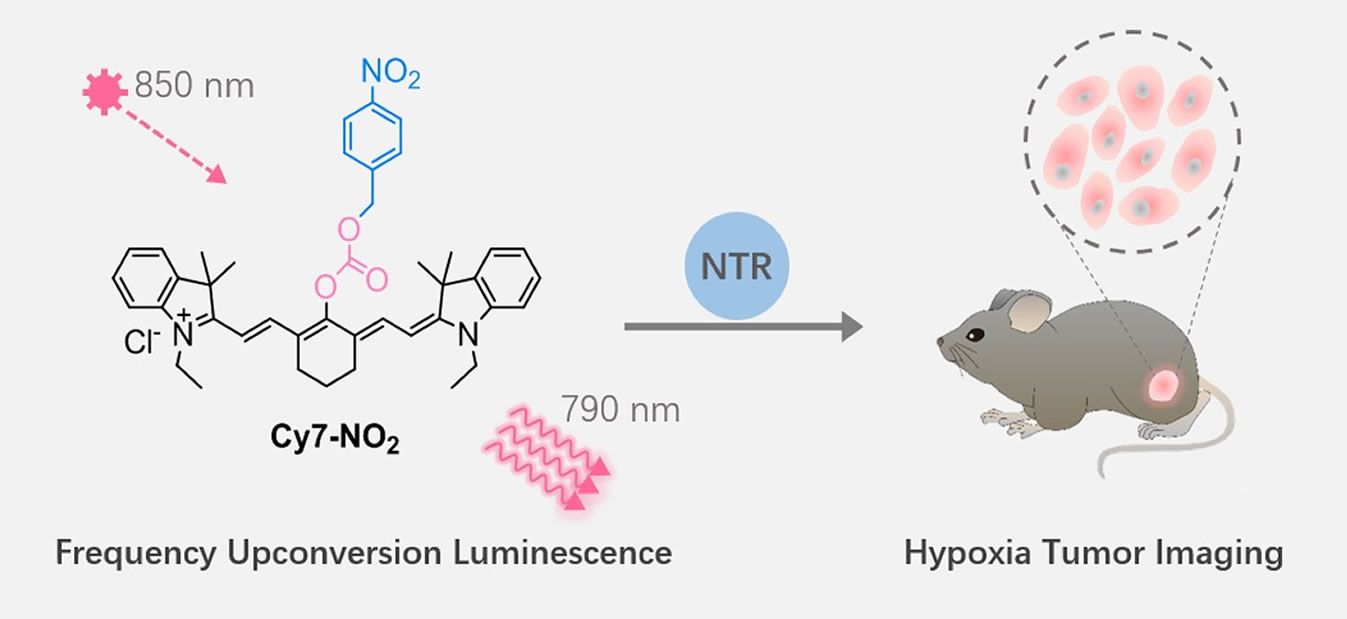
Recently, the Bismuth Research Team in the College of Science achieved a breakthrough in the detection of hypoxic tumors by adopting a unique frequency upconversion method. The results were published in the internationally renowned academic journal, Sensors and Actuators B (SCI, IF: 5.667).
Cancer is currently the main factor affecting human life span. Treatment of cancer, in addition to surgery, usually takes the form of radiation or chemotherapy. However, ischemic and hypoxic tumors are less sensitive to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, resulting in less effective or even ineffective treatment. Therefore, the evaluation of the hypoxic level of tumors is particularly important before radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and the detection of tumor hypoxia markers is a simple and effective way to do so. Among various hypoxic tumor markers, Nitroreductase (NTR) can be overexpressed in a hypoxic solid tumor. The research team led by Professor Miao Yuqing used a near-infrared (NIR) frequency upconversion luminescence (FUCL) probe (Cy7-NO2) based on a cyanine structure decorated with an aromatic nitro group to detect NTR. The FUCL method exhibited a lower detection limit and a higher signal-to-noise ratio, which proves as a breakthrough in the detection of hypoxic tumors. The detection method has a simple preparation of reagents, low requirements on instruments, and can quickly distinguish hypoxic tumors. This achievement is likely to be further applied in the field of biomedical testing.
The first author of the paper, Associate Professor Li Yuhao, specializes in bio-nanomaterials, molecular imaging and nano-diagnostics, and organic small-molecule biosensors. He has published more than 30 papers in internationally renowned journals, such as the Journal of the American Chemical Society and Nanoscale. Among them one paper has an impact factor of over 10 and six over 5.
Led by Professor Miao, the Bismuth Research Team is mainly engaged in the study of bismuth, nano-biomedicine and materials. The current research focuses on nano-medicine, anticancer drugs, antibacterial materials and photocatalysis.