Recently, Lian Zichao, a distinguished professor at the School of Materials and Chemistry of our university, published a research achievement titled "Photoself Fenton Reaction Mediated by Atomically Dispersed Ag Co Photocatalysts toward Efficient Degradation of Organic Pollutants" in the German Journal of Applied Chemistry (Angelw.Chem Int. Ed). Lian Zichao is the first author, along with Professor Li Hexing, president of Shanghai Electric Power University, as the corresponding author. USST is the first corresponding unit.
Efficient treatment of toxic and harmful organic pollutants in organic industrial wastewater is related to human health and sustainable social development. At present, the traditional Fenton reaction is widely used in the treatment of organic wastewater. It mainly utilizes the oxidation-reduction reaction between ferrous ions and hydrogen peroxide to produce highly oxidizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby degrading pollutants. However, for the lack of effective degradation pathways and effective selection of active sites, there are still significant challenges in photochemical selective oxidation of pollutants and their complete mineralization.
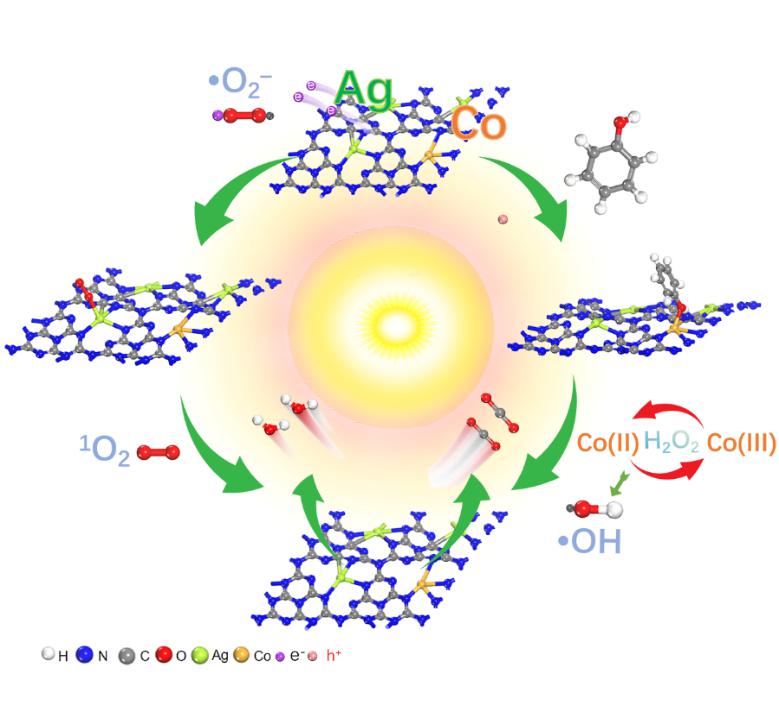
Achieving the complete mineralization of persistent pollutants in wastewater is still a big challenge. The research team propose an efficient photo-self-Fenton reaction for the degradation of different pollutants using the high-density (Ag: 22 wt %) of atomically dispersed AgCo dual sites embedded in Efficient treatment of toxic and harmful organic pollutants in organic industrial wastewater is related to human health and sustainable social development. At present, the traditional Fenton reaction is widely used in the treatment of organic wastewater. It mainly utilizes the oxidation-reduction reaction between ferrous ions and hydrogen peroxide to produce highly oxidizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby degrading pollutants. However, due to the lack of effective degradation pathways and effective selection of active sites, there are still significant challenges in photochemical selective oxidation of pollutants and their complete mineralization.graphic carbon nitride (AgCo−CN). Comprehensive experimental measurements and density functional theory (DFT) calculations demonstrate that the Ag and Co dual sites in AgCo−CN play a critical role in accelerating the photoinduced charge separation and forming the self-Fenton redox centers, respectively. The bimetallic AgCo−CN exhibited excellent photocatalytic performance toward the phenol even under extreme conditions due to an efficient degradation pathway and in situ generation of the hydrogen peroxide producing the main active oxygen species (⋅OH and 1O2) and showed long-term activity in a self-design photo-Filter reactor for the purification of the phenol. Our discoveries pave the way for the design of efficient single-atoms photocatalysts-based photo-self-Fenton reaction for recalcitrant pollutant treatment.
Copyedited by Zhang Liu

 Home
·
News & Events
·
Content
Home
·
News & Events
·
Content