Recently, Dong Yibo, a postgraduate from IPC, published a paper titled “Laser-induced graphene hologram reconfiguration for counter-surveillance multi-secret sharing” in Laser & Photonics Reviews. ( IF:10.947). Luan Haitao, was the first author, academician Gu Min, Dr. Fang Xinyuan and Prof. Chen Xi were the corresponding authors.
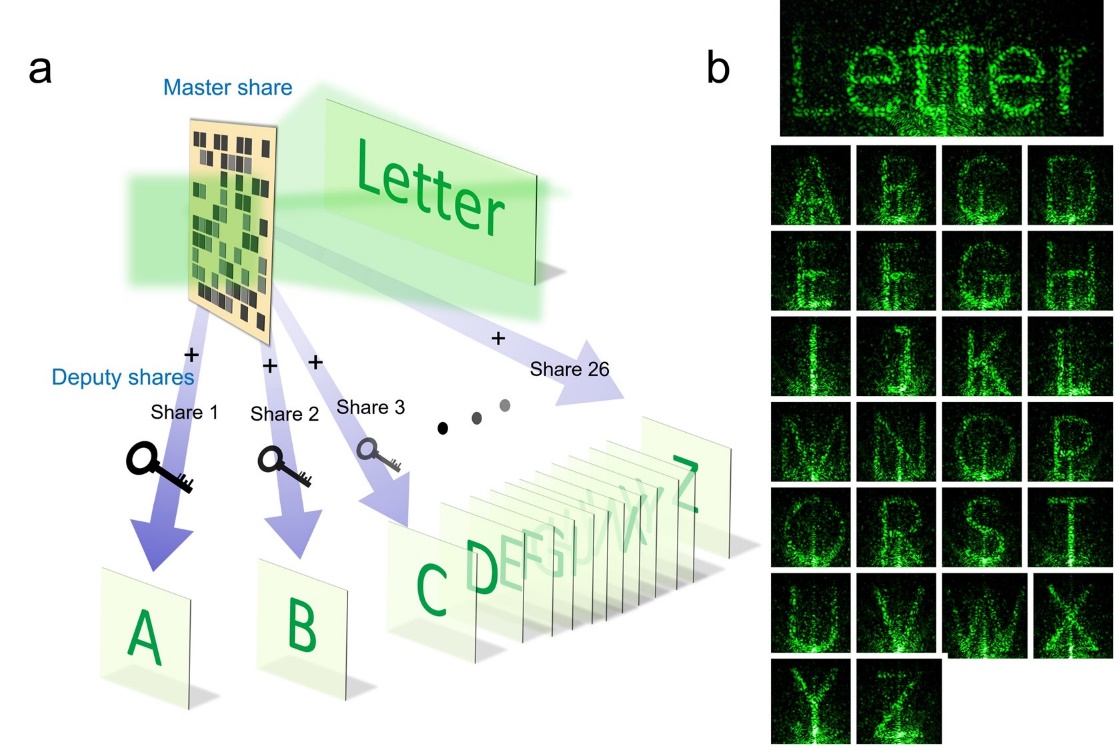
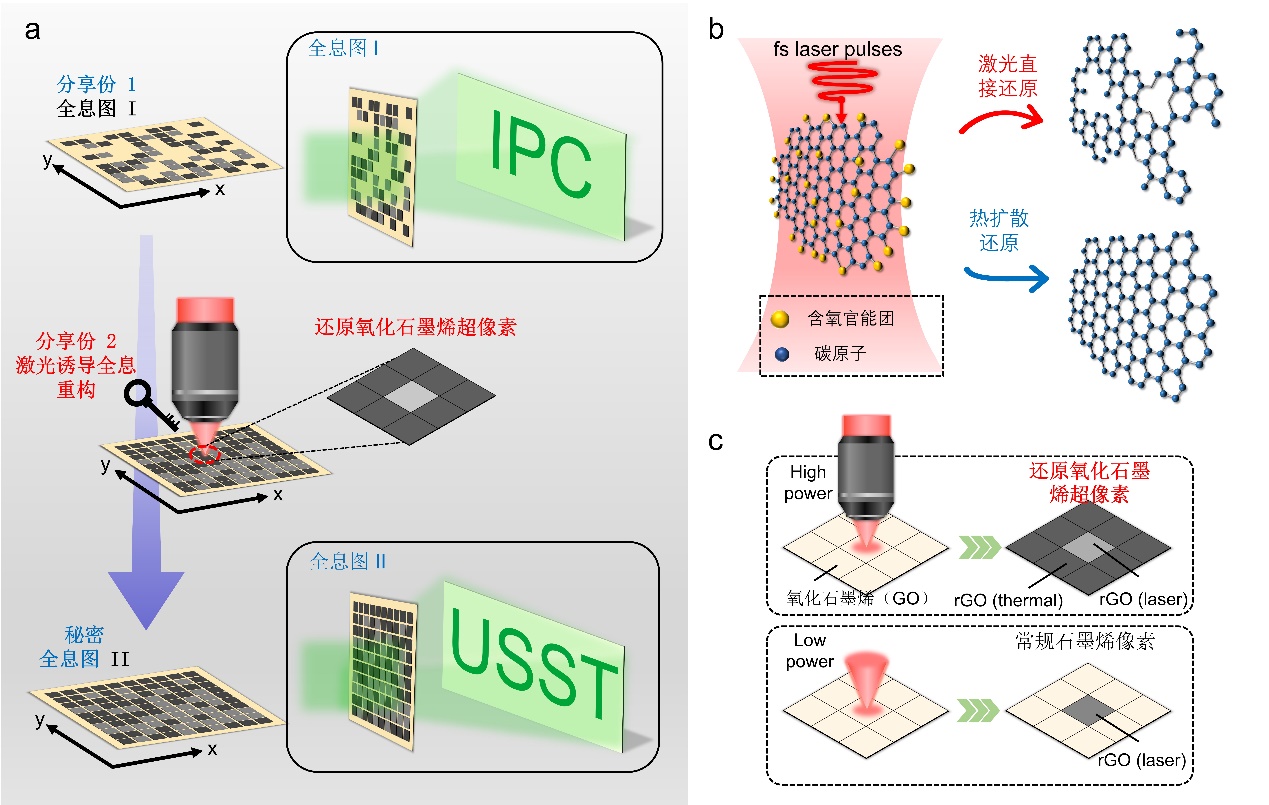
Optical secret sharing is considered as a new generation of high-speed information encryption which is compatible with optical communication. Holography has become one of the most important means of optical encryption. The main form of implementation is to store encrypted information in the form of holograms in optical components and then read with appropriate methods. However, the manufacturing of holographic elements in existing methods has problems of high cost and low efficiency, and these elements can be repeatedly read multiple times, posing a potential risk to information eavesdropping.
In the future, optical encryption devices that are similar to household printers can be developed based on some small laser light sources. Graphene oxide can be used as a medium for information transmission, like the paper we currently use, making it convenient and highly secure to write and read meaages. The holographic reconfiguration technology reported in this article also provides a feasible route for the current reconfigurable research of optical neural networks based on holography. This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission.
Link to the paper: https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.202200805